Differential Effects of Arsenic in Drinking Water on Mouse Hepatic and Intestinal Heme Oxygenase-1 Expression
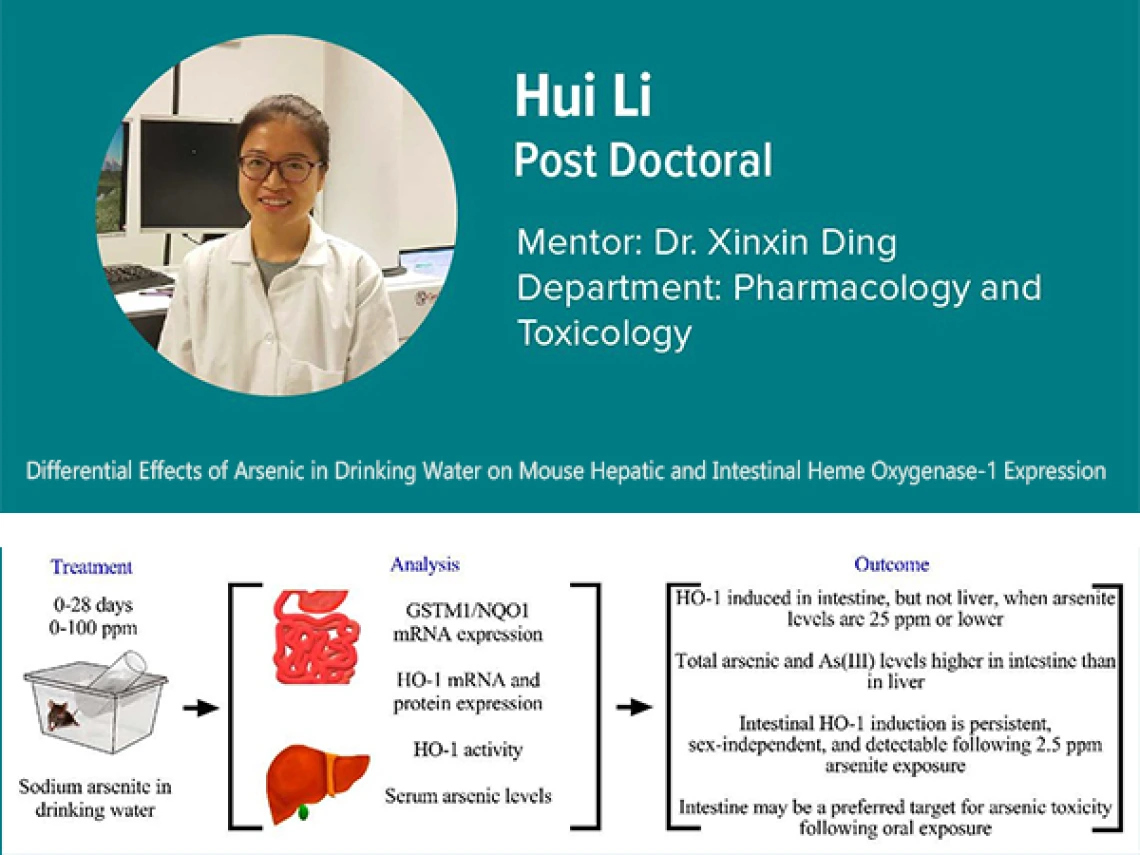
Recent study by Dr. Hui Li, a Post Doc Trainee in Project 2, and colleagues of the University of Arizona Superfund Research Center report novel findings on the effects of arsenic exposure on the expression of heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1), a Nrf2-regulated gene that plays a critical role in the prevention of vascular inflammation, in mouse intestinal epithelial cells and the liver. Intestinal epithelial cells can protect from microbial infections and are the first site of exposure for ingested arsenic, while the liver is a known target of arsenic toxicity.
The expression of HO-1 was determined at mRNA, protein, and enzymic activity levels in mice exposed to sodium arsenite through drinking water, at various doses (0, 2.5, 10, 25, 100 ppm), and for various time periods (1, 3, 7, or 28 days). HO-1 was significantly induced in the intestine, but not liver, at arsenic doses of 25 ppm or lower. The intestinal HO-1 induction was seen in both males and females, plateaued within 1-3 days of exposure, and was accompanied by increases in microsomal heme oxygenase activity. In mice exposed to 25-ppm of arsenite for 7 days, total arsenic and As(III) levels in intestinal epithelial cells were significantly higher than in the liver.
In ongoing studies, they further discovered that the induction of HO-1 expression by arsenic is concentrated in the proximal region of the small intestine, the region connecting to the stomach, with little induction in the distal part, connecting to the large intestine. These findings identify intestinal epithelial cells, particularly those in the proximal region, as likely preferential targets for arsenic toxicity and support further studies on the functional consequences of intestinal HO-1 induction.
Publication:
Li H, Fan X, Wu X, Han W, Amistadi MK, Liu P, Zhang D, Chorover J, Ding X, Zhang QY. Differential Effects of Arsenic in Drinking Water on Mouse Hepatic and Intestinal Heme Oxygenase-1 Expression. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Sep 18;11(9):1835. doi: 10.3390/antiox11091835. PMID: 36139908; PMCID: PMC9495312.

