Understanding Release Mechanism and Interactions of Cadmium and Arsenic by Simulated Digestion
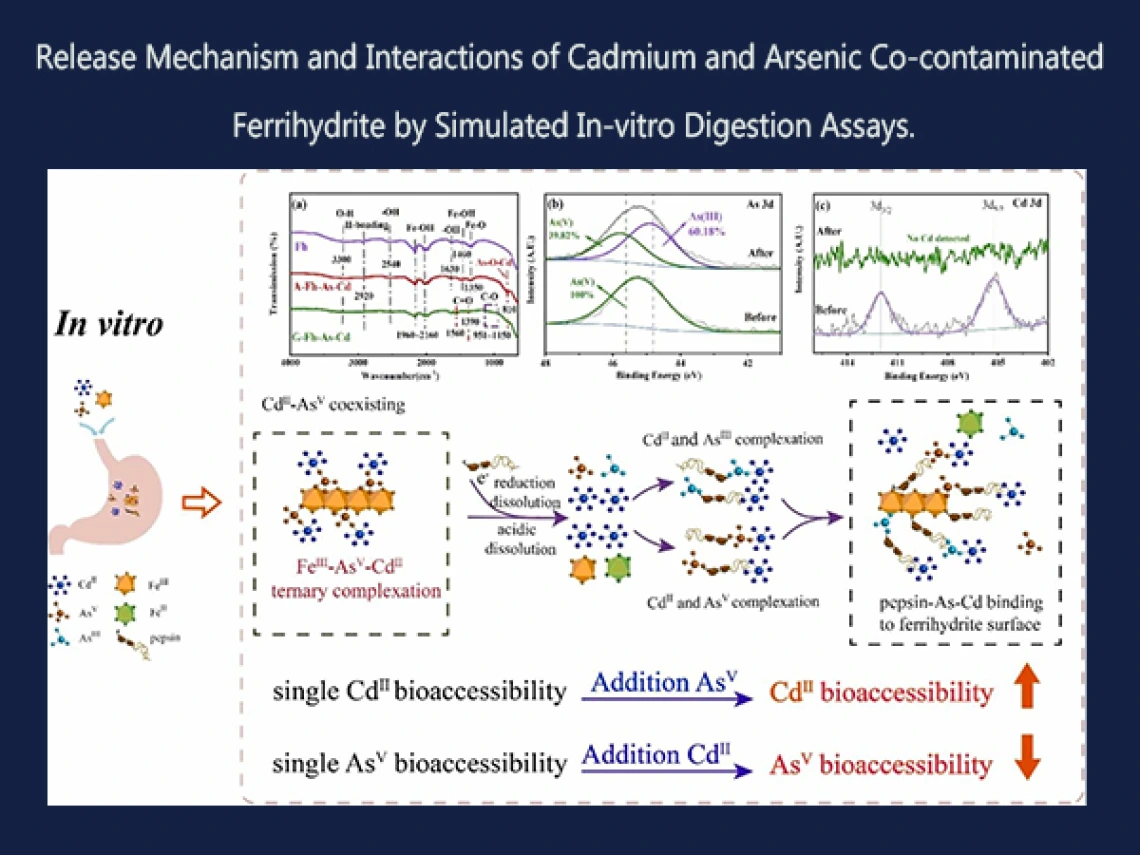
University of Arizona Superfund Research Center (UA SRC) investigators in Project 4 recently published the results of a study that investigated the interaction mechanism of ferrihydrite-adsorbed cadmium (Cd) and arsenic (As) in gastric simulated bio-fluid.
Cadmium (Cd) and arsenic (As) co-contamination is widespread and threatens human health, therefore it is important to investigate the bioavailability – when a substance enters circulation in the body and has an active effect – of Cd and As co-exposure. Currently, the interactions of Cd and As by in vitro assays, or studies of biological matter outside normal biological context, are unknown. In this work, the team of researchers studied the concurrent Cd-As release behaviors and interactions with in vitro simulated gastric bio-fluid assays.
This study aims to:
- investigate Cd and As speciation and release in gastric bio-fluid using ferrihydrite as model surface sorbent mineral.
- reveal the role of pepsin in Cd and As liberation in vitro.
- determine the enhancing or suppressing phase partitioning behavior for Cd-As co-sorbed ferrihydrite.
Understanding synergistic enhancement or detraction of in vitro bioaccessibility of Cd and As in coexistence systems will inform health risk assessments in muti-metal(loid) contaminated sites.
This study deepens the understanding of health risks from Cd and As interactions during environmental co-exposure of multiple metal(loid)s. The findings have important implications for the development of potential regulatory strategies for multi-metal(loid) co-contaminated dust and soil.
Publication:
Bai B, Kong S, Root RA, Liu R, Wei X, Cai D, Chen Y, Chen J, Yi Z, Chorover J. Release mechanism and interactions of cadmium and arsenic co-contaminated ferrihydrite by simulated in-vitro digestion assays. J Hazard Mater. 2024 Apr 5;467:133633. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2024.133633. Epub 2024 Jan 26. PMID: 38335617; PMCID: PMC10913812.

